Social Media Depression Study
The researchers recruited more than 500 undergraduate students who frequently use social media to complete an anonymous online survey that measured both depressive symptoms as well as specific types of social media behaviors. The association between social media use and means of log depressive symptoms was stronger for girls compared with boys test for interaction p 0001.
 Have We Created Unsocial Media Kaspersky Official Blog
Have We Created Unsocial Media Kaspersky Official Blog
From there the answers were coordinated with a depression assessment tool.
Social media depression study. Social media SM use is increasing among US. We surveyed 1787 adults ages 19 to 32 about SM use and depression. Researchers studied the behavioural habits of.
One such study from 2015 saw researchers concluding that social media can cause anxiety and depression which could lead to poor sleep quality intensifying the problem. Social Media Use Linked to Developing Depression Research Finds Dec 10 2020 College News In the News Young adults who increased their use of social media were significantly more likely to develop depression within six months according to a new national study authored by Dr. Previous studies have stated that excessive social media use can maybe contribute to depression says Ceballos.
According to a study published in the Canadian Journal of. Social media use increases depression and loneliness study finds. Studies also indicate that social media may trigger an array of negative emotions in users that contribute to or worsen their depression symptoms.
Facebook and other social media platforms impact on self-esteem is disputed among research for example Mehdizadeh 2010 found a negative correlation between Facebook engagement and self-esteem however it must be noted that this study was limited by having subjectivity in. Brian Primack dean of the College of Education and Health Professions and professor of public health at the University of Arkansas. Everyone experiences not having the perfect body image the perfect grades or the popularity.
In this study we sought to identify distinct patterns of social media use SMU and to assess associations between those patterns and depression and anxiety symptoms. The earliest studies related to social media use and depression began to appear around 2013. Defining Depression Clinical depression or major depressive disorder is a mood disorder characterized by ongoing feelings of sadness and loss of interest in activities that an individual once enjoyed.
The previous studies primarily focused on social media envy the length of time spent on social media. One of their main findings was that higher amounts of social media use were associated with higher levels of depression. Steers 2016 postulates that social media has functions which decrease depression due to a sense of social capital.
Social media use and screen time can lead to an increase in depression and anxiety among teens and adolescents a new study finds. In October 2014 a nationally-representative sample of 1730 US adults ages 19 to 32 completed an online survey. The social media platforms analyzed in the questionnaires included Facebook YouTube Twitter.
Based off of a newsletter named Healthline they discovered that over 350 million people in the United States suffer from depression. Brian Primack dean of the College of Education and Health Professions and professor of public. Among girls greater daily hours of social media use corresponded to a stepwise increase in depressive symptom scores and in the proportion with clinically relevant symptoms.
A new Canadian study has drawn a link between social media screen time and depression in teenagers. Young adults who increased their use of social media were significantly more likely to develop depression within six months according to a new national study authored by Dr. Young adults and its association with mental well-being remains unclear.
Social Media Depression. University of Pennsylvania. Yet there is ample evidence to suggest that social media is associated with depression and other problems such as classroom disruption sleeping disturbances anxiety jealousy and low self-esteem in young adults.
The list goes on. Previously conducted studies that pertain to the relationship between social media use and depression are limited because the field is relatively new. Participants were recruited via random digit dialing and.
There has been a point in someones life where they did not feel good enough. In a previous study done by The American Academy of Pediatrics researchers have coined a term they call Facebook depression a form of depression that forms in adolescents due to plenty of time spent on social media websites such as Twitter and as it is named after Facebook which then leads to leading signs of depression forming O. This study assessed the association between SM use and depression in a nationally representative sample of young adults.
Studies have linked the use of social media to depression anxiety poorer sleep quality lower self-esteem inattention and hyperactivity often in teens and adolescents.
 Study Social Media Increases Depression Cnn Video
Study Social Media Increases Depression Cnn Video
 Social Media Use Linked To Greater Risk Of Depression Among Adult Indonesians Study Coconuts Jakarta
Social Media Use Linked To Greater Risk Of Depression Among Adult Indonesians Study Coconuts Jakarta
Blog Post 2 Mattiesutherlandblog
Cutting Social Media Use To 30 Mins Per Day Significantly Reduces Depression And Loneliness Slsv A Global Media Csr Consultancy Network
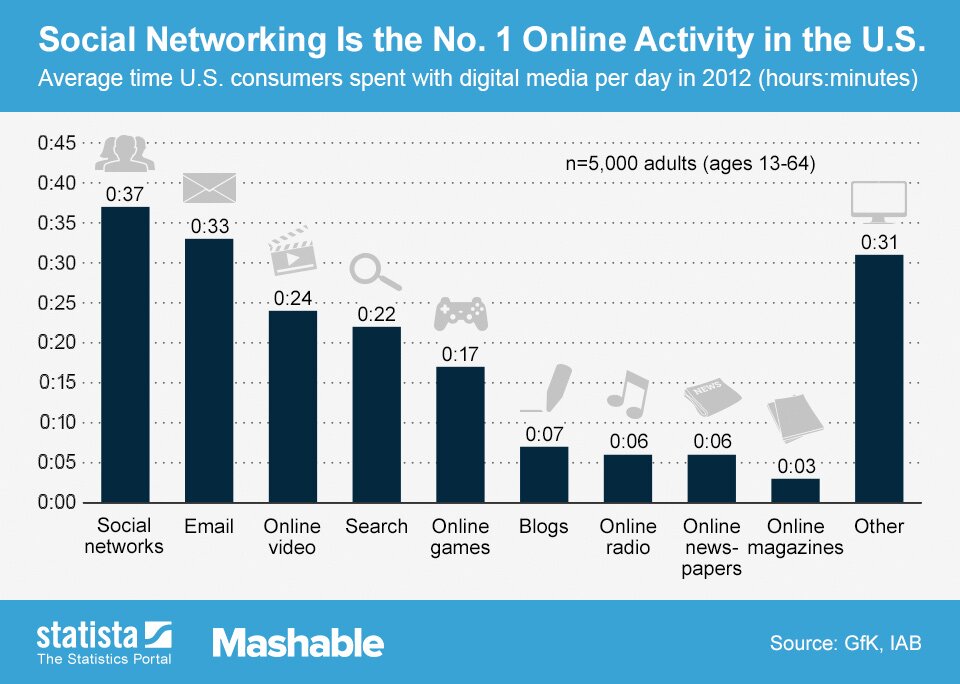 Social Media And Mental Health Siowfa16 Science In Our World Certainty And Controversy
Social Media And Mental Health Siowfa16 Science In Our World Certainty And Controversy
 Social Media Alert Teenage Girls At A Higher Risk Of Depression From Excessive Use Digital Information World
Social Media Alert Teenage Girls At A Higher Risk Of Depression From Excessive Use Digital Information World
 How Heavy Use Of Social Media Is Linked To Mental Illness The Economist
How Heavy Use Of Social Media Is Linked To Mental Illness The Economist
 A Guide To Understanding Social Media And Depression
A Guide To Understanding Social Media And Depression
 Yes Social Media Depression Is Real And Here S How To Deal With It
Yes Social Media Depression Is Real And Here S How To Deal With It
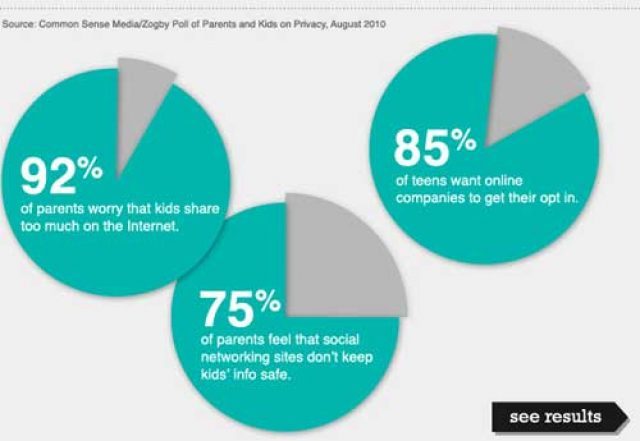 Why Social Media Might Be Causing Depression Global Village Space
Why Social Media Might Be Causing Depression Global Village Space
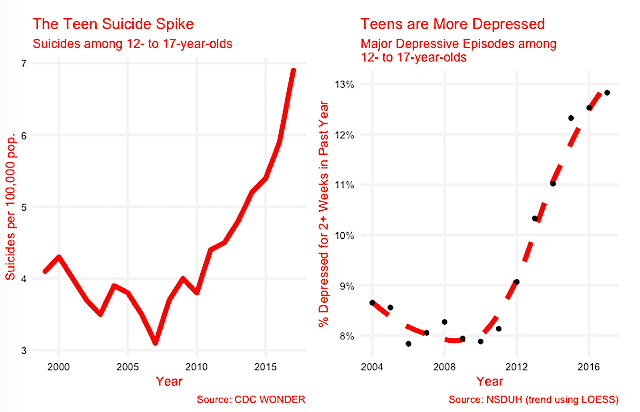 Are Smartphones And Social Media Hurting Our Kids Institute For Family Studies
Are Smartphones And Social Media Hurting Our Kids Institute For Family Studies
 Depression And Social Media Niklas Blog
Depression And Social Media Niklas Blog
 6 Ways To Protect Your Mental Health From Social Media S Dangers Digital Information World
6 Ways To Protect Your Mental Health From Social Media S Dangers Digital Information World
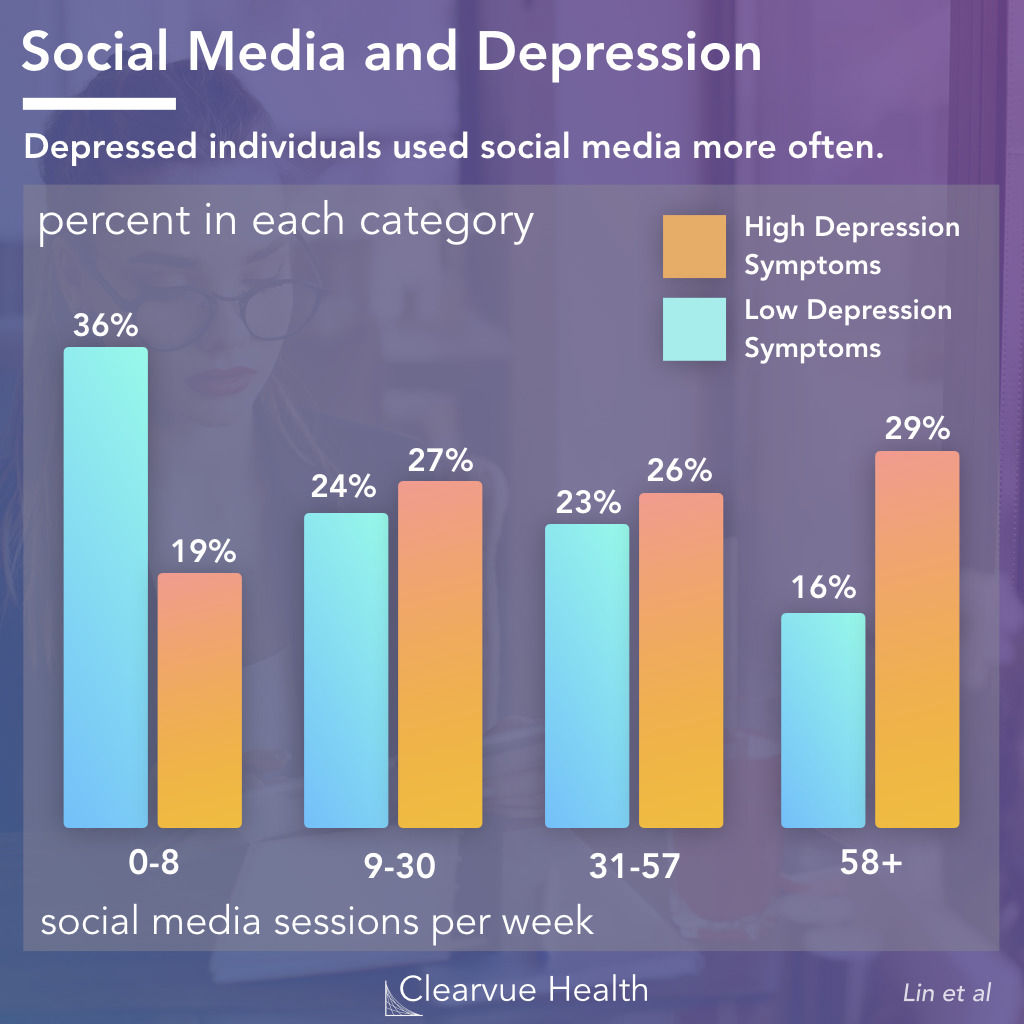 3 Charts Social Media Use And Depression Visualized Science
3 Charts Social Media Use And Depression Visualized Science
Comments
Post a Comment